Cluj-Napoca: Fostering Creativity & Innovation for a Smart City
The Development Strategy of Cluj-Napoca for 2014-2020
Cluj-Napoca, the Heart of Transylvania
- The Economic Capital of Transylvania, Romania
- 0.5 million inhabitants in the metropolitan area
- Academic Center & youthful city – 12 universities, 80.000 students
- Multicultural City
- The Friendliest City in Europe towards foreigners (Eurostat)
- Cultural city & Contemporary Arts center
- Innovation & IT Hub
STRATEGIC DIRECTIONS:
- Development of the city based on principle of “the QUALITY OF LIFE of its inhabitants”
- Balance between economic growth and social cohesion
- Energy-efficient city
- Better urban mobility
- Inclusive city
- Safe city
- Efficient and transparent local administration
Cultural & Creative Industries in Cluj-Napoca
- The creative industries and the university sector are Cluj-Napoca’s economic engines
- More than 15,000 people work in the local IT sector
- 1,300 IT businesses in the city
- the European media refers to Cluj-Napoca as the ‘Silicon Valley of Romania’
- Current key work areas for the majority of IT companies: outsourcing and process optimization => need to shift towards integrated creative products. The need for innovation
- The IT sector needs creativity. It needs the cultural and artistic sectors
Support for Cultural & Creative Industries
The municipal budget for cultural, youth & social projects rose considerably and constantly over the past 6 years: from 368,937 euros (2011) to 3,056,179 euros (2016).
Funding from the municipality has been oriented to subsidise the independent cultural & youth sector (local NGOs) and sometimes to finance specific projects of major cultural institutions in the city. Besides the direct investments allocated to the cultural operators and institutions, in the past 5 years the City Hall invested almost 40 million euros into developing the cultural and touristic capacity of Cluj-Napoca.
Other creative industries (besides IT), like film, design, media and music have had a few rising star projects in recent years. These are potential key advantages and sustainable development strands for our city that need solid and long-term support to flourish.
CREIC – Regional Excellence Center for Creative Industries
- venues/spaces for individuals and SME’s (Small & Medium Enterprises)
- creative individuals and companies will have access to various facilities, financial and judicial services
- our aim: to create a cluster effect that allows competitiveness growth through information exchange, business partnerships, economies by using shared resources (spaces and equipment)
Transilvania Creative Industries Cluster
- the first in Romania
created together with local universities
Cultural & Creative Industries’ Impact – TOURISM
The development of the cultural, arts and entertainment sector in Cluj-Napoca has had a visible impact on tourism. In 2016, the number of tourists in Cluj-Napoca grew by: 15,9% comparing to 2015, respectively 54,19% comparing to 2012.
Cultural & Creative Industries’ Impact – CULTURAL DYNAMICS
Studies by the Research and Consultancy Centre in the Field of Culture constantly place Cluj as the top city in Romania in terms of Urban Cultural Vitality (not including the capital, Bucharest).
Indicators:
- cultural infrastructure
- specialized human resources
- budget allocations for culture/cultural activities
- participation
- creative economy – creative industries support for the non-profit sector (NGOs)
Support for Cultural & Creative Industries
Stage I:
- opening the centre in a historical monument building which will be rehabilitated
- hosting activities in the fields of: research, documentation, preservation, promotion and exhibition, workshops, conferences and other training sessions in the fields of visual arts
Stage II:
- expanding the project to a residency centre – interdisciplinary residency programs for visual artists, performers, architects, designers
- support and involvement from the local technology companies
Double purpose: supporting artistic creation and generating creative projects with practical applications in the social and business environments. Arts and technology will be brought together for new, trans-sectorial and innovative approaches and projects, redefining the boundaries between Arts and Technology.
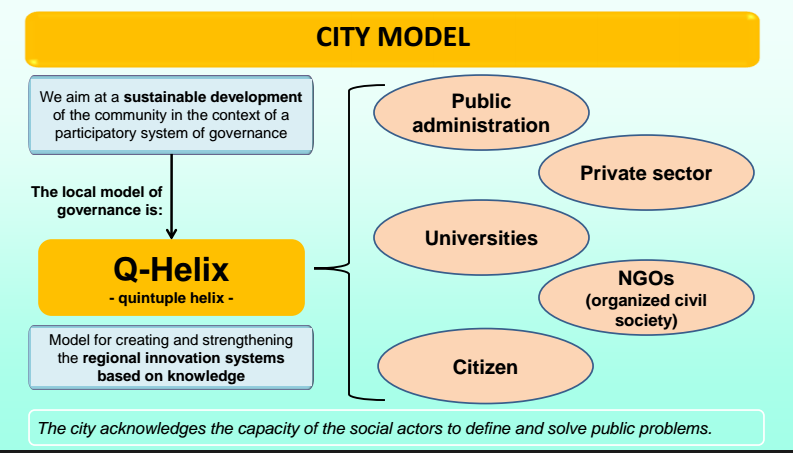
Advisory Council – governance tool
In Cluj-Napoca, we often deal with public problems through consultation networks and we make decisions with the help of experts, NGOs, professional organizations, employers’ associations and the citizens’ input .
Since 2016, the Cluj-Napoca City Hall has an Advisory Council for Entrepreneurship and Innovation in IT, which includes representatives from both IT clusters activating in our city.
The strategy for Cluj-Napoca, smart city – uploading the IT & Smart City Strategy, which is a key project in partnership with the representatives of the IT & C industry of Cluj-Napoca and the local Universities.
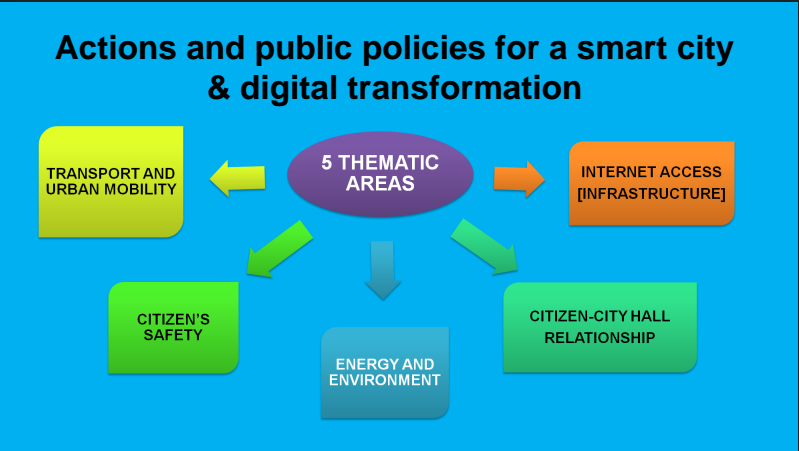
Future projects for Cluj-Napoca, smart city
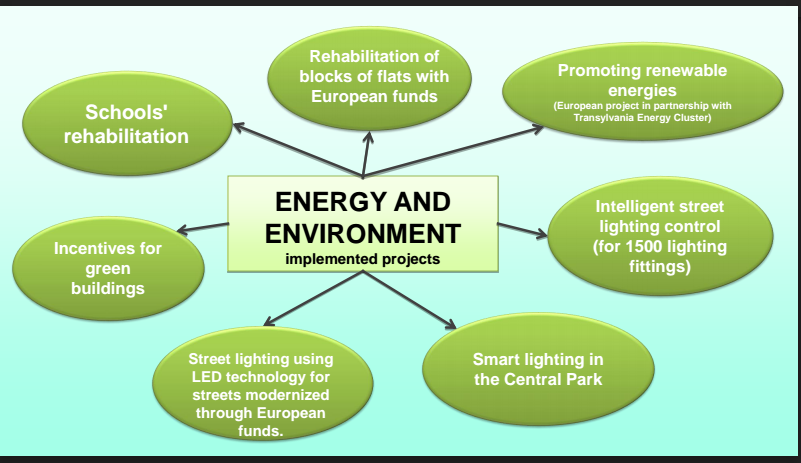
Energy and environment
- 10 electric buses and 3 charging stations + 30 (2019)
- Monitoring and management of the street lighting turn on points
- Modernisation and extension of the public lighting network on 22 streets
- Blocks of Flats thermic rehabilitated through European funds: at least 50 blocks of flats with 1.800 apartments will be rehabilitated by 2020
- Schools’ rehabilitation
Energetic management
- Ongoing program of growing the energy efficiency in the buildings within the city
- Ongoing program of energy evaluation for all public buildings and establishing several investment priorities based on this evaluation
- Implementing an electronic system of monthly collection of consumption data from the public buildings and creating a data base of the consumption utilities
- Organizing a common procedure for buying electric energy for all the public buildings in the city, in order to obtain a better price
- Organizing a local structure with an advisory role reuniting experts from various fields of interest: energy efficiency, private and public sector and NGOs
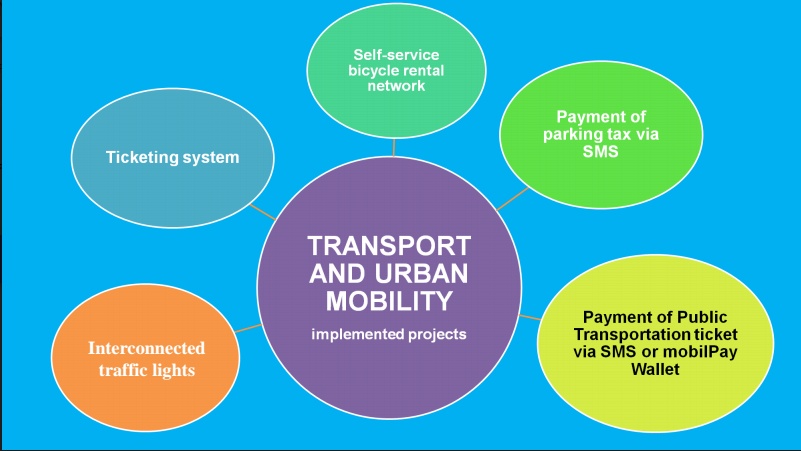
Transport and Urban Mobility
- 2017-2018: buying 50 buses, 10 electric buses, 8 trolleybuses, 16 tramways
- Prioritising the public transportation through dedicated lanes
- Providing information regarding the real-time availability of the means of public transportation
- Providing forecasts regarding real-time traffic
Citizen’s safety
- Implementing a system of sensor in order to monitor pollution and noise
- Data analyzing in order to take actions to reduce different types of road accidents
Other projects for the inhabitants and tourists
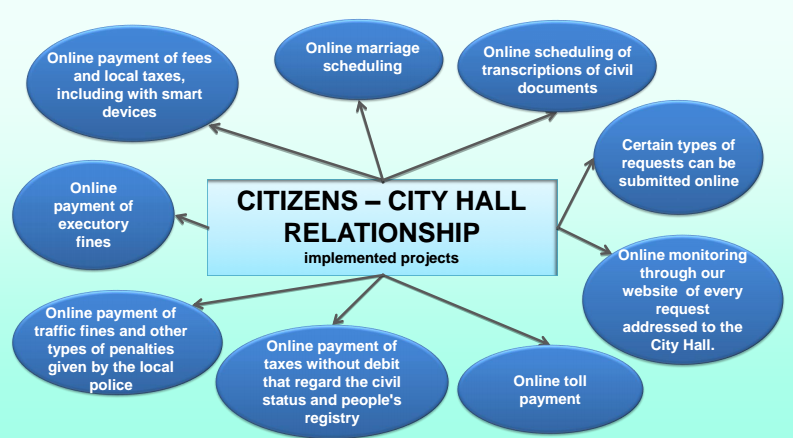
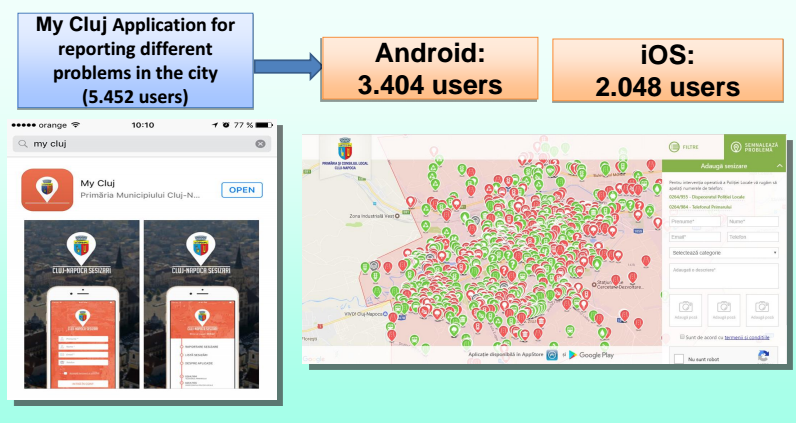
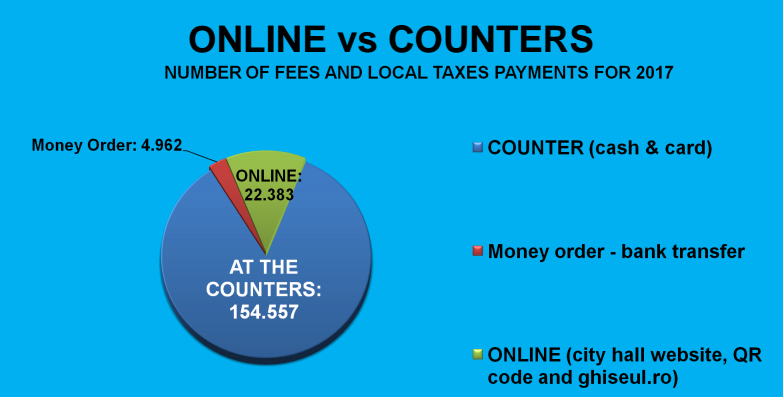
- The City Hall website: interaction platform between citizens and institutions
- Volunteering service in IT
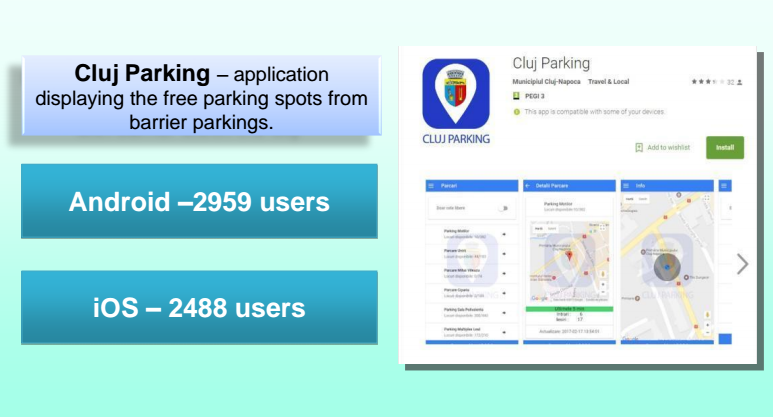
- Online payment of fees for parking with subscription
- Diversification of the payment methods of public parking
- An App for tourism (including guided tours of the city)
Smart Public Services
Transport
- Solutions for the Public Transportation Company in order to give real-time information regarding the public transport (mobile Apps)-> Encourage the citizens to use public transportation
Leisure and Tourism
- Quick and general presentation of the cultural scenery of the city, with events and people’s reviews •An easy way to find daily updated information regarding every important sights
- Easy-to-find touristic-oriented websites and cultural events
- All the information, like opening hours or ticket prices in one place
- Possibility to buy online tickets
Public Health
The use of technology in order to keep in touch with the patients online, monitoring their health and offering public health services
Participatory Budgeting
2013– Pilot participatory budgeting project in the biggest district of Cluj-Napoca: Mănăștur
Result: Cinema Dacia was modernized, so was Mehedinți Street, Primăverii Park and tens of small projects were implemented
2015– Participatory budgeting for young people-Com’on Cluj-Napoca within the project Cluj-Napoca
2015 – European Youth Capital
Result: financing of over 100 projects initiated by the youth.
2017- Cluj-Napoca City Hall: the first in Romania to implement the participatory budgeting with the help of technology (online)
Conclusions
The technology and analysis of data offer solutions to specific problems in fields such as: public transportation, public safety, energy efficiency, sanitation, health, economic development, street maintenance, relationship with the citizens.
Increase the capacity to anticipate the problems that the inhabitants of the city or of the metropolitan area deal with every day.
It is important to use technology to innovate, but it is more important to have an inclusive and collaborative city.
It is important to have smart cities and regions and use the technology to solve the everyday problems. But it is more important to understand that technology is just an instrument and that we need “smart citizens”.
We need a social contract based on the involvement of both social actors and citizens in the decision- making process.
The relationships based on trust between the social partners together with the democratization of the participating to creation and innovation are essential.